A therapeutic swimming program to improve life quality of participants with disabilities acquired
Main Article Content
Abstract
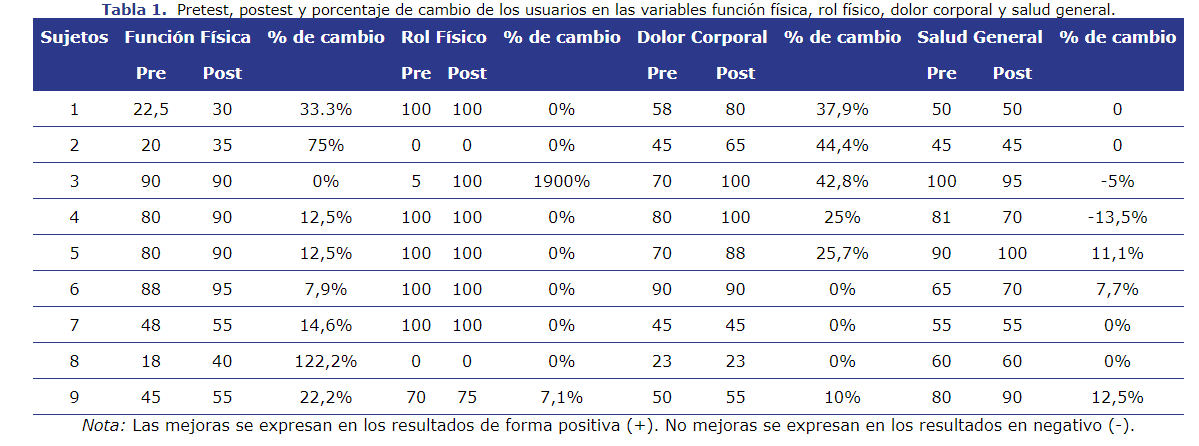
The population with disabilities resulting from accidents or pathologies has increased in the country; and the rehabilitation periods in public hospitals are not sufficient for most cases. Therefore, at the request of the National Rehabilitation Hospital of Costa Rica, a research was done with the objective to design a therapeutic swimming program to improve the quality of life of people with disabilities acquired. It was applied for a year, twice a week, to a group of nine people with different types of acquired disability, referred by the National Rehabilitation Hospital of Costa Rica, as part of the Physical Activity Program Adapted for people with disabilities from the School of Human Movement Sciences and Quality of Life of the Universidad Nacional of Costa Rica. To collect the information, the Health Questionnaire was applied at the beginning and at the end of the program. It was evidenced that the majority of the subjects show improvements in the perception of the dimensions: "Pain," Vitality "," Social Function" and in the "Mental Health" dimension. Therefore, it can be concluded that the therapeutic swimming program contributed to the improvement of the perception of health and quality of life of participants with an acquired disability.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Those authors who have publications with this journal, accept the following terms of the license Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0):
You are free to:
Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation.
No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material.
References
Carrera, P. Y Quijia, D. (2017). Evaluación de la calidad de vida del adulto mayor con hipertensión arterial, del Hogar de Anciano Santa Catalina Labouré y Proyecto 60 y Piquito del barrio Parque Inglés, durante el mes de junio 2017. http://repositorioslatinoamericanos.uchile.cl/handle/2250/2969763.
García, D. M., & López, I. G. (2012). Inclusión social de personas con discapacidad física a través de la natación de alto rendimiento. Apuntes: educación física y deportes, 2012, n.º 110, 4.º trimestre (octubre-diciembre), pp. 26-35 (110), DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5672/apunts.2014-0983.es.(2012/4).110.03
Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censo (INEC). 2018. Encuesta Nacional sobre Discapacidad 2018. San José, Costa Rica.https://www.inec.cr/sites/default/files/documetos-biblioteca-virtual/reenadis2018.pdf
Jacobs, P. (2009). Effects of resistance and endurance training in persons with paraplegia. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009 May;41(5):992-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19346989/
Jacobs, P. (2014).The effects of upper extremity progressive resistance and endurance exercises in patients with spinal cord injury. Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation, 27(4).https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260682959_The_effects_of_upper_extremity_progressive_resistance_and_endurance_exercises_in_patients_with_spinal_cord_injury
Medeiros, I.S.; (2019), NATAÇÃO COMO FORMA DE INCLUSÃO: APLICANDO O MÉTODO HALLIWICK EM PESSOAS COM DEFICIENCIA AUDITIVA. XIII Coloquio Internacional “Educação e Contemporaneidade”. Educon, Aracaju, Volume 13, n. 01, p.1-12. Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.29380/2019.13.04.13
Moreno, M. (2005). Educación Física en el discapacitado. Colombia: Editorial Lexus.
Vilagut, G.; Ferrer, M.; Rajamil, L.; Rebollo, P.; Permanyer G.; Quintana, J.M.; Santed, R.; Valderas. J.M.; Rivera, A.; Domingo, A. y Alonso. J. El Cuestionario de Salud FS-36 español: una década de experiencia y nuevos desarrollos. Gaceta Sanitaria, Barcelona, 2005; 19 (2): 135-50. http://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0213-91112005000200007
Wendel-Vos, G.C.W., Schuit, A.J., Feskens, E.J.M., Boshuizen, H.C., Verschuren, W.M.M., Saris, W.H.M., et al. (2004) Physical Activity and Stroke. A Meta-Analysis of Observational Data. International Journal of Epidemiology, 33, 787-798. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyh168.